This article was written a decade ago. A few things may be outdated, but the process still works for most installations today, in 2025.
![]()
What is VirtualBox?
VirtualBox is a virtualization software that allows you to run other operating systems like Windows, Linux and others as guest operating systems. There are mainly two operating systems involved.
- Host Operating System - This is the current resident operating system (OS) that's running on your computer right now.
- Guest Operating System - This is the new operating system we'll install on top of VirtualBox (after we install VirtualBox).
This article will focus on installing Windows 7 as the guest operating system under Mac OS X or Windows.
Wait a minute. Why would I need to run Windows under my current copy of Windows (or Mac OS X)?
- To install or test software without installing it in your primary OS
- If you have this beta version of a new game that you want to try out without endangering your current installation
- To run certain programs on multiple copies of Windows without buying multiple computers
- If you and your friends share one computer and you want want to install a coupon printer software on multiple Windows installations so that each of you gets your daily quota of coupons
- To run programs that won't run on your current OS.
- If you want to run a Windows game or a great software on your Mac, but it runs only on Windows.
To get started, you'll need the following:
- VirtualBox installer (dmg, exe)
- Windows ISO file or bootable Windows CD/DVD
- Decent Internet connection
1. Installing VirtualBox
1.1 Download the installer
The download link is at https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads
If you're running Windows, download the exe file beside VirtualBox 4.3.14 for Windows hosts
If you're running Mac OS X, download the dmg file beside VirtualBox 4.3.14 for OS X hosts
As of August 28, 2014, the version of VirtualBox is 4.3.14.
1.2 Start the installation
Double-click on the installer and start the installation. If you're on Windows and it shows a security warning, click on "Run". You may temporarily lose Internet connectivity during the installation.
2. Installing Windows 7 under Virtualbox
Hopefully you have a Windows CD lying around somewhere. If you can get hold of an ISO file, that would be great too.
2.1 Start up VirtualBox
- In the Oracle VM VirtualBox Manager, click on New and then on Continue.

- Under Create New Virtual Machine, enter "Windows 7" under the Name field. The Operating System should automatically change to Microsoft Windows and the Version to Windows 7.

- Under Memory, set the base memory size to 1 GB if your computer has 4GB of RAM or more. Enter 1024 MB as base memory size.
- Under Virtual Hard Disk, let it take the default recommended size of 25GB for the start-up disk. Make sure that Create New Hard Disk is selected.
- Select VDI in the next screen.
- Under Virtual disk storage details, select the default option Dynamically allocated. Click on Continue.
- You'll be taken to the Summary screen. Your screen should look like this:

- Under Summary, click on Create.
- In the confirmation page, click on Create.
This is what the VirtualBox Manager should look like at this point.

Let's point this virtual machine (VM) to the Windows ISO. We have our ISO at C:ISO/win7.iso
- In the VirtualBox Manager, while Windows 7 is selected, click on Settings.
- Select the tab Storage. You should see this:
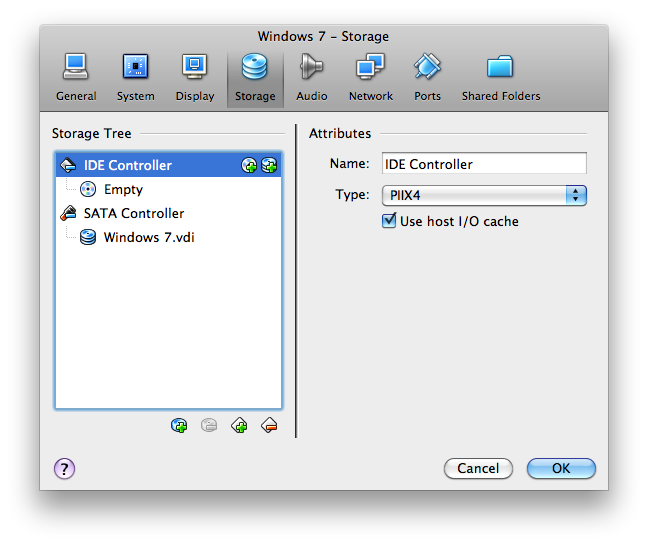
- Click on the first + button in the same line as IDE Controller. When you hover your mouse over it, it should say "Add CD/DVD Device".
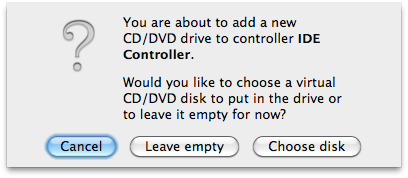
- In the popup, select "Choose disk".
- Navigate to the folder containing your Windows 7 ISO file and select it. Click on Open.
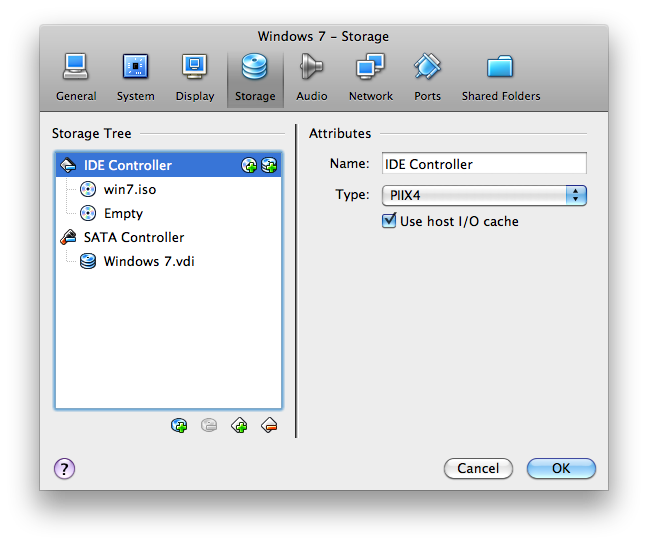
- The ISO file will show up in the Storage tab like this.
- Now, go to the VirtualBox Manager screen and click on Start with the green arrow.
- You'll see this "Auto capture keyboard" warning.
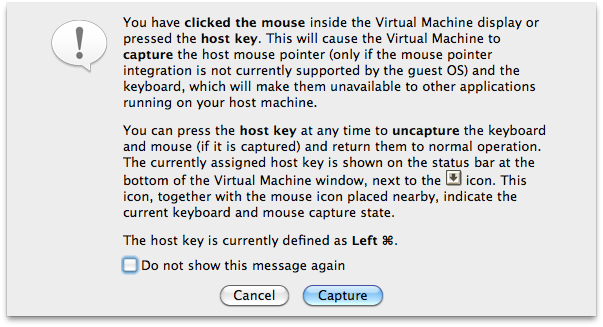
This means that whenever you switch from host OS to guest OS, anything you type will be sent to the guest Windows 7 which you are about to install. Make a note of the host key because you'll have to be able to switch from the guest Windows 7 back to the host OS.
For Mac OS X, the default host key is the left command ⌘ key. For Windows, the host key is the right Ctrl key. If you get stuck anywhere, just click on the host key+I, and the cursor control will be back to the host OS.
Changing Host Key (Mac OS X)
I usually like to change the host key in the Mac to the right command key because I use the left command key with tab to switch applications and it interferes with my shortcuts.
For that, go to VirtualBox Manager, and in the top menu, click on VirtualBox → Preferences → Input tab.
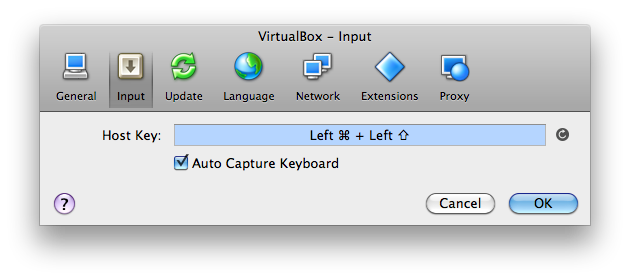
Change the host key by clicking on the right command key. Then say "Close", and you'd have set the right command key as the hot key.
Start the Windows installation
- Finally, start the Windows installation.
- Click on Install now. It will take around 20 minutes depending on your computer speed and what applications are open.

Network settings
By default, the network is set to NAT, which lets you access the Internet from within the guest Windows. But you can't access the guest from the host. If you want to be able to share data back and forth, start by changing the Network to Bridged.

- Go to Machine → Settings and select Network.
- It will say "Attached to NAT". Change it to Attached to Bridged Adapter.

- Click OK.
- Your guest Windows will be treated as a separate computer on the network and get its own IP address.
Related Posts
If you have any questions, please contact me at arulbOsutkNiqlzziyties@gNqmaizl.bkcom. You can also post questions in our Facebook group. Thank you.